The importance of airport slot governance
- Like
- Digg
- Del
- Tumblr
- VKontakte
- Buffer
- Love This
- Odnoklassniki
- Meneame
- Blogger
- Amazon
- Yahoo Mail
- Gmail
- AOL
- Newsvine
- HackerNews
- Evernote
- MySpace
- Mail.ru
- Viadeo
- Line
- Comments
- Yummly
- SMS
- Viber
- Telegram
- Subscribe
- Skype
- Facebook Messenger
- Kakao
- LiveJournal
- Yammer
- Edgar
- Fintel
- Mix
- Instapaper
- Copy Link
Posted: 4 November 2024 | Robson Freitas | No comments yet
For International Airport Review, Robson Freitas, Head of Operations, Security, and Airport Emergency, and Felipe Brandão Operational Planning Analyst at Belo Horizonte International Airport explore the importance of airport slot co-ordination, the global standards governing it, and the role of new technologies in enhancing the efficiency of air travel.
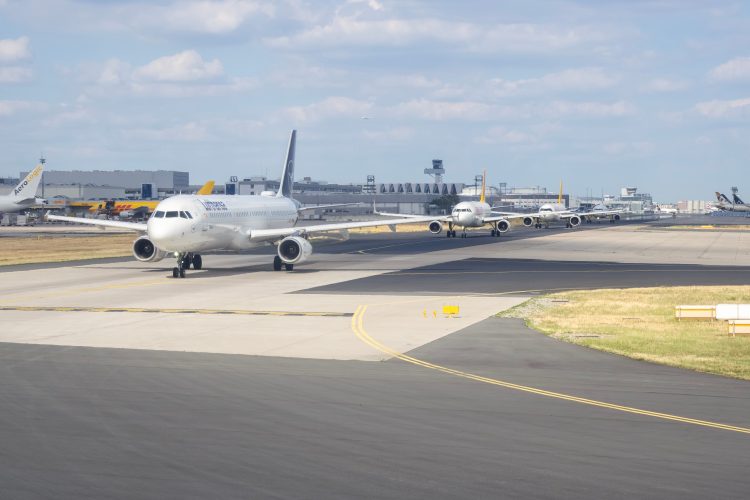


Do you know what an airport slot is?
Airport slots are time intervals allocated for an aircraft to take off or land at an airport. These times are carefully planned to maximise the use of airport infrastructure and minimise conflicts between flights. Slot co-ordination is especially important at busy airports, where demand for flight times can exceed available capacity.
The International Air Transport Association (IATA) defines an airport slot as permission granted by a co-ordinator for a planned operation to use the full range of airport infrastructure required to arrive at or depart from an airport at a specific date and time.
Note: An airport slot is not the same as an Air Traffic Control (ATC) slot.
Where is a slot required?
All airlines must have a slot allocated to arrive at or depart from a Level 3 airport.
- Level 1
- The airport’s capacity generally meets demand
- No co-ordination is required at a Level 1 airport.
- Level 2
- The airport may experience congestion during certain times of the day, week, or season
- Schedule adjustments are made through mutual agreement with the airlines.
- Level 3
- Demand at the airport significantly exceeds its capacity,
- All airlines and aircraft operators must receive a slot allocation from an independent slot co-ordinator to arrive at or depart from the airport.
Airport slot co-ordination
Airport slot co-ordination is a critical process for ensuring the efficiency and safety of air traffic. With the constant increase in the number of flights, effective management of slots—specific times assigned for take-offs and landings—has become crucial to prevent congestion and delays. This process allocates the limited capacity of an airport to airlines before each scheduling season, ensuring that airline schedules can be planned according to the available airport capacity. This helps avoid unnecessary delays on the day of travel and optimises the efficient use of this highly sought-after infrastructure when fully implemented.
Airport slot governance
IATA is actively involved in a range of activities to ensure a transparent, sustainable, flexible, and reliable slot allocation system.
- Working with governments and regulators to promote and align policies with the Worldwide Airport Slot Guidelines (WASG)
- Closely collaborating with Airports Council International (ACI) and the Worldwide Airport Co-ordinators Group (WWACG) to ensure that slot policies and processes evolve while remaining practical, harmonised, neutral, non-discriminatory, and effective in managing airport capacity constraints
- Supporting the implementation of a single global standard
- Organising the International Slot Conference biannually to allow airlines to meet with scheduling facilitators and slot coordinators in person to review their slot portfolios and finalise their future schedules.
Worldwide Airport Slot Guidelines (WASG):
The Worldwide Airport Slot Guidelines (WASG) form the cornerstone of the global airport slot co-ordination process. Published collaboratively by IATA, Airports Council International (ACI), and the Worldwide Airport Co-ordinators Group (WWACG), the WASG upholds principles of transparency, flexibility, certainty, consistency, and sustainability. Regular updates and revisions ensure that the WASG reflects internationally recognised best practices, guaranteeing that airport slots are allocated fairly and impartially to airlines through standardised policies and procedures.
Source: https://www.iata.org/en/programs/ops-infra/slots/slot-guidelines/
Slot Conference
The Slot Conference (SC) is a major business event that draws over 1,300 delegates, including representatives from more than 300 capacity-constrained airports, over 250 airlines, and 90+ sponsors and exhibitors from around the world. Held twice a year, it is one of IATA’s largest gatherings, rotating locations globally. Since its inception in 1948, the conference has become a key event in the aviation industry calendar, providing the global airline community with a platform for rapidly optimising their schedules and exploring new opportunities for route and network expansion. The primary aim of the conference is to help airlines secure the slots needed to create the best possible schedules for their customers at co-ordinated airports.


Pictures of the Slot Conference Brazil in Belo Horizonte – August 2024. C: BH Airport
Source: https://www.iata.org/en/programs/ops-infra/slots/conference/
How is airport slot co-ordination managed in Brazil?
Airport slot co-ordination aims to regulate access to infrastructure at congested airports, seeking to align the demand for air operations with the available airport capacity. The National Civil Aviation Agency (ANAC) serves as the co-ordinator responsible for slot allocation at co-ordinated airports in Brazil. This co-ordination activity is conducted with independence and adheres to the principles of transparency, non-discrimination, impartiality, and efficient use of declared airport capacity.
ANAC began managing slot allocation at Brazilian airports in 2009, with the goal of applying internationally recognised rules for airport co-ordination at Guarulhos Airport (GRU/SBGR). Since then, ANAC has achieved the following:
- Co-ordinated 11 airports for the 2013 Confederations Cup
- Co-ordinated 5 airports for the 2013 World Youth Day
- Co-ordinated 25 airports for the 2014 FIFA World Cup
- Co-ordinated 8 airports for the Summer 2016 (S16) season due to the Rio 2016 Olympic and Paralympic Games.
Currently, ANAC is responsible for the co-ordination of five airports in Brazil:
- Congonhas (CGH/SBSP)
- Guarulhos (GRU/SBGR)
- Pampulha (PLU/SBBH)
- Recife (REC/SBRF)
- Santos Dumont (SDU/SBRJ).
In addition to the co-ordinated airports, there are airports declared by ANAC as “facilitated,” where the co-ordination and allocation of airport infrastructure are managed by the airport operator itself. There are currently eight facilitated airports:
- Brasília (BSB/SBBR)
- Confins (CNF/SBCF)
- Florianópolis (FLN/SBFL)
- Fortaleza (FOR/SBFZ)
- Galeão (GIG/SBGL)
- Porto Alegre (POA/SBPA)
- Salvador (SSA/SBSV)
- Viracopos (VCP/SBKP).
To standardise the airport infrastructure allocation process, all concessionaires are now following the same deadlines and procedures used for co-ordinated and facilitated airports. This includes Infraero and the concessionaires AENA, BH Airport, CCR Aeroportos, Inframerica, RIOGaleão, Viracopos, Vinci Airports, and Zurich Airport Brasil.
Resolution Nº 682 of June 7, 2022: This Resolution regulates airport co-ordination and establishes rules for the allocation and monitoring of airport infrastructure usage.
Source: https://www.gov.br/anac/pt-br/assuntos/regulados/empresas-aereas/slot
Slot co-ordination involves several key steps:
- Capacity planning: Assessing the airport’s capacity in terms of runways, gates, and ground resources
- Slot allocation: Distributing available slots among airlines, taking into account factors such as passenger demand and operational efficiency
- Monitoring and adjustments: Continuously overseeing slot usage and making adjustments as needed to accommodate changes in flight operations.
Challenges in slot co-ordination
Slot co-ordination faces various challenges, including:
- Variable demand: flight demand can fluctuate significantly throughout the year, necessitating frequent adjustments to slot allocations
- Conflicts of interest: airlines may compete for slots during peak times, requiring a fair and transparent allocation process
- Regulations: slot co-ordination must comply with both international and local regulations, adding complexity to the process.
National Slot Conference in Brazil
ANAC hosts the National Slots Conference twice a year, aiming to enhance the efficient use of Brazil’s airport infrastructure. The conference is an integral part of the slot co-ordination and allocation process for each season, enhancing the effectiveness of schedule adjustments for airlines operating in the country. It enables more efficient and timely operations by optimising the airlines’ air network.


Pictures of the Slot Conference Brazil in Belo Horizonte – August 2024 C: BH Airport.
Between August 14 and 16, Belo Horizonte hosted the National Slots Winter 2024 Conference, organised by the National Civil Aviation Agency (ANAC) with support from BH Airport. During this event, airlines, other coordinated and facilitated airports, and the air traffic control authority (Brazilian Air Force) participated in planning Brazil’s air network for the winter 2024 season, which runs from October 27, 2024, to March 29, 2025.
The event, which is technical in nature, includes several sessions for slot adjustments, arrival and departure times at airports co-ordinated by ANAC in the country. Airlines aim to optimise their schedules according to their needs. Co-ordinated airports are those where the expected air traffic demand exceeds the currently available capacity, leading to operations that require a scheduled time for passing a fixed point or for landing or take-off (slot).
The importance of slot planning and coordination arises from the need to secure landing and take-off times at various airports within the network, including those co-ordinated by ANAC where airport infrastructure is in high demand.
Innovations and the future
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in slot co-ordination. Advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence tools are being used to forecast flight demand and optimise slot allocation. Additionally, collaboration between airports and airlines is becoming more integrated, fostering further efficient air traffic management.
Conclusion
Airport slot co-ordination is a crucial component of the global aviation system. By embracing new technologies and collaborative practices, it is possible to address challenges and ensure that air traffic growth is managed in an orderly and efficient manner.
As we see demand for air transportation returning to its pre-pandemic levels, it is extremely important that the use of airport infrastructure is managed efficiently – and slot management is one way of doing this. At the end of the day, an efficient transportation system brings benefits not only to the people who use it, but also to the economy and society of a region.
About the authors


C: BH Airport
Robson Freitas began his career in the early 2000s as a Flight Operations Officer, working for major Brazilian airlines. He was involved with the FIFA World Cup Organising Committee in Brazil, where he supported the air operations for National Teams. During the RIO2016 Olympic and Paralympic Games, he managed the airport operations centre at Rio de Janeiro International Airport. Since 2018, Robson has served as Head of Operations, Security, and Airport Emergency at Belo Horizonte International Airport. In this role, he oversees daily operations, ensures high-quality customer service, and maintains operational efficiency, adherence to the ACDM process, and regulatory compliance. In 2022, he completed the Global ACI-ICAO Airport Management Professional Accreditation Programme (AMPAP), becoming the sixth Brazilian to earn this certification.


C: BH Airport.
Felipe Brandão is a Transportation Engineer with master’s degree in Transportation Infrastructure from the University of São Paulo (USP). He has experience in road maintenance planning and regulatory monitoring for some road concessionaires in Brazil, such as Triunfo Concebra and CCR Nova Dutra.
Since 2022, he has been working at Belo Horizonte International Airport as Operational Planning Analyst. He is responsible for the slot co-ordination process at the airport, negotiating airport slots with the airlines. He also monitors the use infrastructure, develops continuous improvement projects and identifies investment triggers based on the projected demand.
Issue
Related topics
Air traffic control/management (ATC/ATM), Airport development, Airport leadership, Airside operations, Conferences and events, Innovation, Passenger experience and seamless travel, Passenger volumes
Related airports
Belo Horizonte International Airport, Brasília International Airport (BSB), Confins–Tancredo Neves International Airport, Congonhas-São Paulo Airport (CGH), Florianópolis International Airport – Hercílio Luz (FLN), Fortaleza Pinto Martins International (FOR), Pampulha–Carlos Drummond de Andrade Airport, Porto Alegre’s Salgado Filho International Airport (POA), RIOgaleão - Tom Jobim International Airport (GIG), Salvador Bahia Airport (SSA), Santos Dumont Airport (SDU), São Paulo Guarulhos International Airport (GRU), Viracopos International Airport (VCP), Zurich Airport Brasil
Related organisations
Airports Council International, FIFA, International Air Transport Association, The National Civil Aviation Agency, Worldwide Airport Co-ordinators Group